This is the follow up post for SEO Tips for Websites Templates part 1. In this post we discuss how to optimize each segment of your web pages to create an optimal, streamlined website template.
Template Optimization Tips by SEO Design Solutions
Web Page Variations are Typically Constituted By:
- The header or masthead
- The body area
- Columns which separate the body (1,2,3 or 4)
- And the footer
Based on the information contained within each region, different weights are applied from the perspective of SEO to assign a higher search engine position based on the content, page strength and reputation of that page.
Each one of these regions is broken into a block, search engines use block segmentation analysis and other methods to assess and grade the value of each types of information within each block; this in turn impacts the overall relevance score for that page.
Page Layout Options:
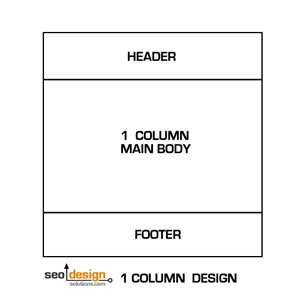
1 Column Pages are Ideal for Product Pages
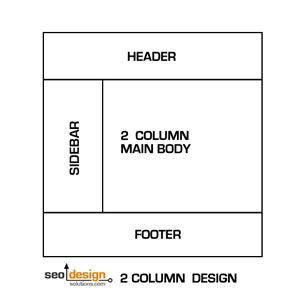
2 Column Designs are Common for Blogs and Sites
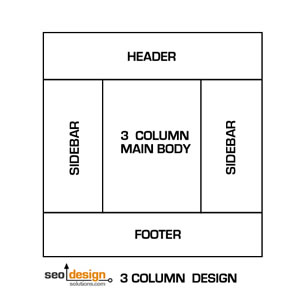
3 Column Designs are Typical For Sites with a Vast Array of Content (such as news sites) or sites with Multiple Products
Rather than consume a page whole, segmentation algorithms treat each region with unique filters such as structural tags (h1-h6), semantic blocks, navigation blocks, etc., to determine which blocks receive more weight in correlation to calculating relevance.
Now, it’s just a matter of (a) not producing too many overlapping areas (b) knowing which segments carry more weight and (c) tying them together in a logical and structured format to produce optimal search engine results.
Optimizing Your Sites Header:
- Hard code links when possible using absolute URLs into your navigation http://www.domain.com/page.html vs. relative URLs /page.html – this will pass link flow as a referrer as well as ensure you minimize 404 errors (broken links), if you’re using dynamically pulled data to populate the navigation schema.
- Avoid javascript in the navigation and use CSS for javascript like drop downs to ensure spiders crawl, parse and follow the links within navigation (unless you are using contextual linking or secondary navigation). Otherwise, you could be putting a major kink in the hose when it comes to feeding your subordinate / child pages by not providing them enough connectivity to the sites spine (which is the main navigation and / or sitemaps).
- Determine competitive keyword thresholds and implement keyword-rich titles where applicable (i.e instead of “black shoes” as anchor, try “black designer shoes” to link to category pages which reflect the keyword / destination) if there is an opportunity to increase relevance without stuffing keywords to compensate for on page content.
- Don’t keep java, javascript or CSS inline (on the page) this only increases load time, instead use the rel=” value and point to resources on the server
<link href="/css-location.css" rel="stylesheet" />or<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://www.domain.com/menu.css" />or use gzip compression for CSS or other data that needs to load in advance (such as images or stylesheets). Here is a great Gzip http compression plugin if you use WordPress that does this in a snap.
Optimizing the Body Region:
- Use an h1 tag with the exact match 2 or 3 keyword variation you intend to rank for.
- Establish prominence by using the keyword you intend to rank for within the first 25 words in the body area. This works best if surrounded by other contextual synonyms that reinforce topicality.
- Ensure that each page has enough unique content to separate it from the other site segments “such as a heavy header, common sidebar or common footer elements”. Each of the other regions can inadvertently be packed full of dozens of links and skew the focus of the page (since all the keywords, data and links overlap).
- If you are using dynamic sidebars or other server side includes that pull from a database, try to segment each page as much as possible to eliminate duplicity as much as possible and link from themed pages to themed pages (related products to category pages or other related product pages). The more original and unique each page is, the better. When in doubt, limit the number of inbound to outbound links and ensure the page links to either (a) the sitemap (b) the parent page or (c) the homepage to recycle the link flow the page has acquired from both on page and off page factors.
- Use text to provide “keyword-rich” anchor text/links to other pages themed to rank for the keywords in the anchor text (every occurrence of blue shoes in body text across the site, links to the domain.com/blue-shoes.html page).
- Reduce images through jpeg compression to make sure load times are minimal. Also make sure to use alt attributes for images, particularly if those images are links (which can also serve as secondary navigation).
- Limit dynamic API’s from taxing the body area that have to wait for other sites to populate or respond in order for the rest of your site segments to load (things like social media buttons, etc. can all sap performance and load time, which is becoming more important as a metric for rankings).
- Don’t stuff keywords or link excessively from the body area, one link for every 100 words is acceptable, anything exceeding this may hemorrhage vital ranking factor from contextual links.
Optimizing Columns or Sidebars:
Common uses for sidebars are to provide related links via block quotes or anchor text for sub navigation. They can also house widgets, API’s from other sites, advertisements, images and / or text to funnel traffic to other pertinent regions of a website.
Considerations for Secondary Columns or Sidebars:
- When applicable try not to reuse common areas across the entire site. Create a unique set of server side includes that you can pull dynamically in the sidebar or footer that change based on the page or site segment you are on. There are many ways to do this, such as using a tiered breadcrumb like trail for site navigation or using related links based on site structure and relevance (lateral linking across mfg’s, linking up to categories, etc.).
- Instead of linking out excessively site wide, consider consolidating links on category pages and then having one link to those category pages to showcase multiple options (instead of linking out dozens of times on each page).
The takeaway is:
- Make the main body area the focal point for content, context and relevance.
- Reinforce that with an h1 tag, SEO friendly naming conventions that match the preferred ranking, h1 and internal links to the page.
- Segment each sidebar to reflect what is relevant to the user on THAT page, but try to limit the link loss from having common recurring elements across the entire site (which only creates internal duplicate content and pushes pages supplemental).
- If you are forced to repeat the same elements across a block on multiple pages within the global site architecture, then eventually search engines algorithms will normalize their occurrences by creating a null set (which prioritizes the information). Sometimes this is not avoidable, but in some instances, using a more suitable lean template is a solution to add more weight to the page and increase its relevance score for the focal point in the main body (which is the main region scored in tandem with the title and links from algorithms for context).
Optimizing the Template Footer:
Footers provide a way to elect pages with the most significance within a site when you need to create additional prominence for specific landing pages.
Considerations for the Footer Region:
- Have multiple variations to match the site segment so you do not emulate the same footer across every page in the site. This makes it easier for search engines to assign relevance to individual pages and not have to pick and choose from several potential sources of similar content (since the sidebar, header and footer are packed full of text and or links).
- Keep the links manageable (under 100 including navigation), the more links there are leaving a page, the closer that page should be to the root folder unless you intend to build sufficient deep links from other sites to that subfolder to placate relevance and link flow.
- Always link to a local (folder based) sitemap or to a global / master sitemap from the footer regardless of which page you are on. If spiders find it, it will use (a) the links on the page and (b) the sitemap to find new pages, index them and their links and add the scoring methodology to the pages it discovers.
Obviously, this is merely an overview, but aside from writing volumes on each subject, combined with the previous post “SEO Tips for Website Templates” this is at least enough to set the stage and whet your appetite for more information on the topic, or hire someone to execute these types of strategies and SEO services on your behalf.










Wow!
I’ll read this a couple more times (great info).
1) Do you suggest to H1-tag the Title, the entire body, or both?
I always H1-tag the Title, should I be tagging the Body?
2) Would it be ok to mix up the blog Title & the permalink to something like this:
A) Blog Title = “The Best Black Designer Shoes you can Buy”
B) Permalink = “http://myblog.com/black-designer-shoes/”
Or, would it work against me?
Thanks, for the great info!
I hope your answer to #2 in my last comment will be, it’s ok to change the Title & permalink. :)
I have a new blog & this is what I’ve already done on 130+ blog post…
Hey Slimjim:
Glad someone appreciates the content enough to comment. Not trying to be a Guru here, but damn writing this stuff and giving it away for free is time consuming, so, glad you took it to heart.
About h1 and permalinks:
John Lamansky our WordPress mastermind wrote a few insightful posts about WordPress SEO Tips (just type wordpress seo tips in Google it’s #1) in addition to being the genius who implemented SEO Ultimate.
Anyway, John’s input is on his WordPress SEO Tips Post under Tip #14:
https://seodesignsolutions.com/blog/seo-resources/20-practical-seo-tips-to-super-charge-your-wordpress-blog/ Permalinks>
Hope this helps…
hello , i’m just starting in this world of blogs
I’ve been into SEO recently and gathering helpful information for this.
and after reading your post it has become a little easier to me , thanks
Hey Slimjim:
Here is a post that provides more insight about title and meta tag synergy…
https://seodesignsolutions.com/blog/how-to-reference-material/how-to-optimize-meta-titles-and-descriptions/
But in the instance you suggested above, I would put the main keyword first, then a tag-line.
Black Designer Shoes, Buy Affordable Black Designer Shoes at “company”.
Jeffrey,
Thanks, for the reply + links! :)
I really like the link you posted with all the tips, like the tip how to deep link when someone scrapes your RSS. Kinda makes me want to encourage scrapes, lol.
I have a lot more reading to do (here on your blog), & I do appreciate all the work you put into this blog.
Thanks,
Informative blog that gives the step by step procedure of optimizing segments of site such as: header, body region, columns or sidebars and template footer of the webpage. Search engine optimization is highly essential and people can follow these steps to increase page ranking for the webpage.
Thanks for the detailed description.Recently my company launched a website templates section of it’s website and this is indeed a very helpful post as it explains the relevance of SEO with regard to website templates.
Thanks to write for this information in this blog,its more benefits for blog readers,please write more about search ingine optimition(seo)
Hello
I have just read that part 1 for website templates.This Part 2 is full of effective tips for website templates.There is good description in detail as its very easy to understand.Thanks..
Excellent posts Jeffrey (Parts 1 and 2). Would you say it’s always best to provide the content first to the search engines (using CSS) no matter what the layout might look like from a user perspective? Also, I read an article about first link priority some time ago, which some people were saying must be something that will be fixed soon as it heavily counted the first link on a page even if it was nofollow. Do you think this is an issue that needs to be addressed when creating a template?
Thanks for your excellent posts Jeffrey. I’m here every day so certainly appreciate the time you take to write and publish them on your blog.
Justin
@Justin:
Thanks for your comments…
Using CSS to serve up content first is always nice, however, I am not certain that search engines treat is any different (they are evolving at an alarming rate.
Previously link sculpting was a big deal along with first link priority, but once again, the degree in which the information is treated can be vector based and therefore linear metrics do not always apply.
I can say on a practical note to only use links where applicable and to keep the anchors succinct and direct (vs. trying to have several links with overlapping context going to different pages).
The main takeaway is to get past heavy templates and make EACH page unique or at least define it’s market focus beyond a shadow of a doubt.
This means if you have a heavy footer, sidebar or header, then make sure the body text has enough volume and context to define that page, otherwise, it may end up supplemental or diffused from the other shingles (groups of words) on the page.
Thanks again for visiting.
Superb Indexation is the first step in SEO and SERP (search engine result page) domination starts with building an optimal website template.
Thank you a lot for this article!
thanks you ser I will used this seo for my wordpress blog now you can see my blog and please give me your advis
Thanks for the wonderful SEO tips….. its very helpful for our website and blog.
I was exactly looking for such guide as I am planning to build it my own way. I want to design a structure that require to put less efforts in terms of seo.